How to optimize traffic flow in SG 🇸🇬; hackathon solution
I recently took part in a Hackathon which was about developing solutions for Urban mobility in Singapore. Urban mobility involves public transport, private cars, bikes, and other vehicles. It involves traffic flow and public services like MRT.
Business Problem 💰
Use LLMs to help traffic planners respond better in case of an accident, a line breakdown or unforeseen situations like fire or traffic jam.
Currently the decision making in these scenarios are not driven by data but by intuitive understanding of different areas in Singapore, such as where is the nearest fire station from the point of incident or nearest hospital in the area.
Using LLM on the dataset collected by the Land and Transport Authority (LTA) in Singapore can help making these decisions more effective in stressful situations.
Proof of Concept
Before moving on to coding, let me share the final product which might give some context on what is coming next. For now, I am yet to deploy the application on cloud. So you can clone the repo and run this application on your machine.
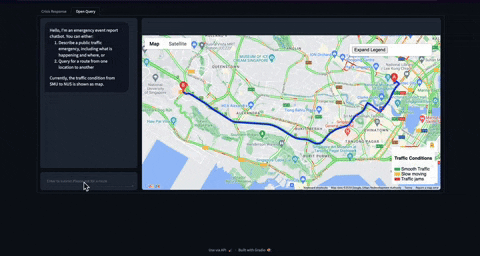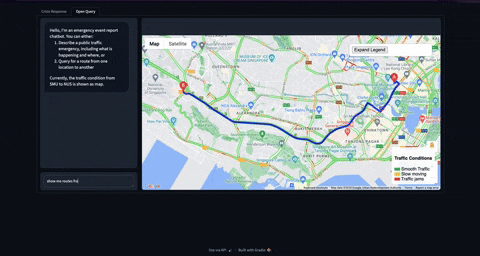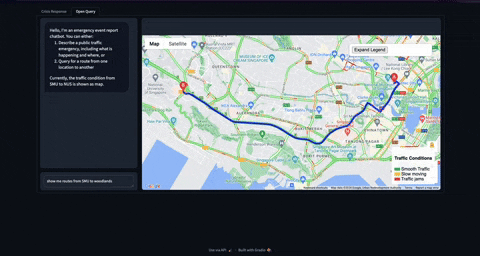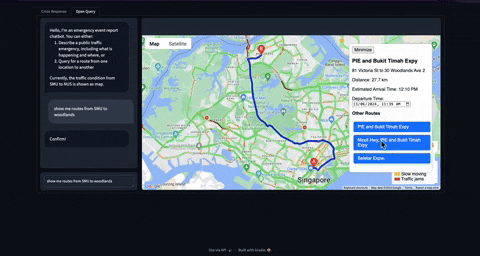
Check out this github repo
Approach and Dataset 🍇
While coming up with the solution, my team first studied the dataset collected by LTA. They maintain both dynamic and static datasets which can be used by researchers or developers.
Dynamic datasets
- Approved road works and faulty traffic lights
- Bus routes and bus arrival
- Bus Service
- ERP rates
- Passenger volumns by train stations and bus stops and more…
Static datasets
- Annual age distribution of buses
- Annual Estimated Mileage for Private Motor Vehicle
- Annual Motorcycle Population by Make
- Annual Motor Vehicle Population by Type of Fuel Used and more…
We decide to use the LTA API to access these datasets and load them on our local database in SQL. Once, loaded, we would use LLM to query on the dataset to find out important information such as which area has the most traffic today, or which station has the highest number of passenger volumn.
We can achieve that by tuning the LLM query into a SQL statement and run it on the database to get data and create daily visualizations.
Load datasets into SQL
Below is the function to autoload static datasets (csv files) into SQL.
def load_data_into_mysql(table, table_path):
conn = pymysql.connect(host=MYSQL_HOST, user=MYSQL_USER, password=MYSQL_PASSWORD, db=MYSQL_DB)
df = pd.read_csv(table_path)
columns = df.columns.tolist()
placeholders = ', '.join(['%s'] * len(columns))
columns_str = ', '.join(columns)
sql = f"INSERT IGNORE INTO {table} ({columns_str}) VALUES ({placeholders})"
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
for index, row in df.iterrows():
cursor.execute(sql, tuple(None if pd.isna(row[column]) else row[column] for column in columns))
#cursor.execute(sql, tuple(row[column] for column in columns))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print(f"Data loaded into {table} table successfully")
Create SQL tables
Of course we would need to create tables in the SQL database before loading the data. Below are some tables for example:
create table traffic_incidents (
Type varchar(255) not null,
Latitude double not null,
Longitude double not null,
Message varchar(255) not null primary key,
Date_time varchar(255) not null
);
create table faulty_traffic_lights (
AlarmID varchar(255) not null,
NodeID varchar(255) not null,
Type int,
StartDate datetime,
EndDate datetime,
Message varchar(255),
constraint faulty_traffic_lights_pk primary key (AlarmID, NodeID)
);
create table road_openings (
EventID varchar(255) not null primary key,
StartDate datetime,
EndDate datetime,
SvcDept varchar(255),
RoadName varchar(255),
Other varchar(255)
);
Get data from LTA with API
In order to get the data from the API, we need to read the json file and convert it into csv and then load it into our sql using the autoload function above.
#this makes call to one dataset at a time
def obtain_data_per_dataset(data_source_name):
response = requests.get(datasets[data_source_name], headers=headers,data=payload)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
if 'value' in data:
df = pd.DataFrame(data['value'])
return df
else:
response.raise_for_status()
Convert query into SQL statement
Until now we are able to get the data from LTA through the API and store in the SQL server on our local machine. At this point we need to use the LLM to convert query to SQL statement. We will be doing that with SQLAlchemy FAISS and Langchain.
def get_sqlalchemy_url():
gcp_project = "nus-competition"
client = bigquery.Client(project=gcp_project)
dataset = "Traffic"
return f'bigquery://{gcp_project}/{dataset}?'
class LLMSQLInterface:
def __init__(self):
sqlalchemy_url = get_sqlalchemy_url()
self.db = SQLDatabase.from_uri(sqlalchemy_url)
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
self.toolkit = SQLDatabaseToolkit(db=self.db, llm=self.llm)
self.bq_inserter = BQDataInserter()
self.df_insert = None
self.examples = [
{"input": "How many road incidents are there today?",
"query": "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_incident FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.traffic_incidents` WHERE Message LIKE CONCAT('(', DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%d/%c'), '%');"
},
{"input": "How many traffic incidents are there today?",
"query": "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_incident FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.traffic_incidents` WHERE Message LIKE CONCAT('(', DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%d/%c'), '%');"
},
{"input": "How many road incidents are there yesterday?",
"query": "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_incident FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.traffic_incidents` WHERE Message LIKE CONCAT('(', DATE_FORMAT(NOW() - INTERVAL 1 DAY, '%d/%c'), '%');"
},
{"input": "How many traffic incidents are there yesterday?",
"query": "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_incident FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.traffic_incidents` WHERE Message LIKE CONCAT('(', DATE_FORMAT(NOW() - INTERVAL 1 DAY, '%d/%c'), '%');"
},
{"input": "How many road works are there today?",
"query": 'SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_roadworks FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.road_works` WHERE StartDate <= CURDATE() AND EndDate >= CURDATE();'
},
{"input": "Which area experienced the most number of road works?",
"query": "SELECT RoadName AS Area, COUNT(*) AS total_roadworks FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.road_works` GROUP BY RoadName ORDER BY total_roadworks DESC LIMIT 1"
},
{"input": "What is the traffic condition now?",
"query": "SELECT RoadName, Volume, HourOfDate FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.traffic_flow` ORDER BY Date, HourOfDate DESC LIMIT 10;"
},
{"input": "How many car parks are available in the star vista right now?",
"query": 'SELECT AvailableLots FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.carpark_avail` WHERE Development = "The Star Vista";'
} ,
{"input": "Where can I find the most car park in Orchard area?",
"query": 'SELECT MAX(AvailableLots) As MaxLots FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.carpark_avail` WHERE Area = "Orchard";'
},
{"input": "How is the traffic flow today?",
"query": "SELECT RoadName, Volume FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.traffic_flow` WHERE Date = CURDATE() ORDER BY HourOfDate DESC LIMIT 10"
},
{"input": "What is the estimated travelling time from Orchard Road to Havelock?",
"query": "SELECT StartPoint, EndPoint, EstTime FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.estimated_travel_times` WHERE StartPoint LIKE '%Orchard%' AND EndPoint LIKE '%Havelock%';"
},
{"input": "How many bus stops are there along Victoria Street?",
"query": "SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(BusStopCode)) AS TotalBusStop FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.bus_stops` WHERE RoadName = 'Victoria St';"
},
{"input": "Which road has the least number of bus stops?",
"query": "SELECT RoadName, COUNT(DISTINCT(BusStopCode)) AS Total_Bus_Stop FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.bus_stops` GROUP BY RoadName ORDER BY Total_Bus_Stop, RoadName ASC LIMIT 5;"
},
{"input": "Which road has the most number of bus stops?",
"query": "SELECT RoadName, COUNT(DISTINCT(BusStopCode)) AS Total_Bus_Stop FROM `nus-competition.Traffic.bus_stops` GROUP BY RoadName ORDER BY Total_Bus_Stop, RoadName DESC LIMIT 5;"
},
{"input": "Given the public transport utilization target of 75% by 2030, can we reach the target?",
"query": "SELECT * FROM `nus-competition.Chatbot.public_transport_utilization WHERE year=2030`;"
},
{"input": "Given the emission target for transport of 6,000,000,000 kg CO2 by 2030, can we reach the target?",
"query": "SELECT * FROM `nus-competition.Chatbot.carbon_emission WHERE year=2030`;"
}
]
self.system_prefix = """You are an agent designed to interact with a SQL database.
Given an input question, create a syntactically correct {dialect} query to run, then look at the results of the query and return the answer.
Unless the user specifies a specific number of examples they wish to obtain, always limit your query to at most {top_k} results.
You can order the results by a relevant column to return the most interesting examples in the database.
Never query for all the columns from a specific table, only ask for the relevant columns given the question.
You have access to tools for interacting with the database.
Only use the given tools. Only use the information returned by the tools to construct your final answer.
You MUST double check your query before executing it. If you get an error while executing a query, rewrite the query and try again.
DO NOT make any DML statements (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP etc.) to the database.
Here are some examples of user inputs and their corresponding SQL queries:"""
self.example_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(
self.examples,
OpenAIEmbeddings(),
FAISS,
k=5,
input_keys=["input"],
)
self.few_shot_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(
example_selector=self.example_selector,
example_prompt=PromptTemplate.from_template(
"User input: {input}\nSQL query: {query}"
),
input_variables=["input", "dialect", "top_k"],
prefix=self.system_prefix,
suffix="",
)
self.full_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessagePromptTemplate(prompt=self.few_shot_prompt),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder("agent_scratchpad"),
]
)
self.agent = create_sql_agent(
llm=self.llm,
toolkit=self.toolkit,
prompt=self.full_prompt,
verbose=True,
agent_type="openai-tools",
)
def create_conversation(self, query: str, chat_history: list) -> tuple:
result = self.agent.invoke({"input": query})['output']
chat_history.append((query, result))
cur_timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
self.bq_inserter.create_table()
self.df_insert = pd.DataFrame({
'file_name': ['Database Query'],
'query': [query],
'answer': [result],
'timestamp': [cur_timestamp]
})
self.bq_inserter.insert_dataframe(self.df_insert)
return '', chat_history
Once we have the backend ready, we need to put that in a frontend interface. We used Gradio in this case. As I did not work on creating the gradio frontend, I cannot share the code for that part.
However, I can carry on with creating a incidence reponse feature which will use Google Maps API to show routes with traffic information and alternate routes from point A to B in Singapore.
This feature will also suggest nearest support service based on the type of incident.
Incident response feature 🚗
In order to build this feature, we need to create a React application which can render google maps with alternate routes and information like travel time, distance etc.
Render the SG Map
The Javascript function below will load the Google Maps based on the map ID which can be acquired by an API key.
import {
APIProvider,
Map,
useMapsLibrary,
useMap
} from '@vis.gl/react-google-maps';
import { error } from 'console';
export default function App() {
const mapRef = useRef(null);
var tester=queryString.parse(window.location.search);
const position = { lat: 43.6532, lng: -79.3832 };
return (
<div style=>
<APIProvider apiKey={process.env.GOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEY}>
<Map
ref={mapRef}
gestureHandling={'greedy'}
fullscreenControl = {false}
mapId={process.env.GOOGLE_MAP_ID}
>
<Directions />
<MapLegend />
</Map>
</APIProvider>
</div>
);
}
Render traffic and routes on the Map
Next we need to show the directions on the map itself with alternate routes and real time traffic layer provided by Google Maps API.
const [arrivalTime, setArrivalTime] = useState(null);
var tester=queryString.parse(window.location.search);
let origin, destination;
const toggleOpen = () => {
setIsOpen(!isOpen);
};
const toggleMinimize = () => {
setIsMinimized(!isMinimized);
};
try {
const points = tester.body ? JSON.parse(tester.body) : null;
if (points && Array.isArray(points) && points.length >= 2) {
origin = points[0];
destination = points[1];
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid or missing origin and destination points in the 'body' parameter.");
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to parse 'body' as JSON or invalid data format:", error);
origin = "SMU, Singapore";
destination = "NUS, Singapore";
}
const map = useMap();
const routesLibrary = useMapsLibrary("routes")
const [directionsService, setDirectionsService] =
useState<google.maps.DirectionsService>();
const [directionsRenderer, setDirectionsRenderer] =
useState<google.maps.DirectionsRenderer>();
const [routes, setRoutes] = useState<google.maps.DirectionsRoute[]>([]);
const [routeIndex, setRouteIndex] = useState(0);
const selected = routes[routeIndex];
const trafficLayerRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (!routesLibrary || !map) return;
const ds = new routesLibrary.DirectionsService();
const dr = new routesLibrary.DirectionsRenderer({
map: map,
polylineOptions: {
strokeColor: '#0000FF',
strokeOpacity: 0.8,
strokeWeight: 6
}
});
setDirectionsService(ds);
setDirectionsRenderer(dr);
const trafficLayer = new google.maps.TrafficLayer();
trafficLayer.setMap(map);
trafficLayerRef.current = trafficLayer;
}, [routesLibrary, map]);
useEffect(() => {
if (trafficLayerRef.current) {
trafficLayerRef.current.setMap(map);
}
}, [map]);
useEffect(() => {
if(!directionsService || !directionsRenderer || !departureTime) return;
directionsService.route({
origin: origin,
destination: destination,
travelMode: google.maps.TravelMode.DRIVING,
drivingOptions: {
departureTime: departureTime,
trafficModel: 'pessimistic'
},
provideRouteAlternatives: true,
})
.then(response => {
directionsRenderer.setDirections(response);
setRoutes(response.routes);
if (response.routes.length > 0) {
const durationInSeconds = response.routes[0].legs[0].duration.value;
const estimatedArrival = new Date(departureTime.getTime() + durationInSeconds * 1000);
setArrivalTime(estimatedArrival);
}
});
}, [directionsService, directionsRenderer, departureTime]);
Render alternate routes
We need to recalculate time and render direction in case a new route is selected by the user.
useEffect(() => {
if (routes.length > 0 && routes[selectedRouteIndex]) {
const durationInSeconds = routes[selectedRouteIndex].legs[0].duration.value;
const estimatedArrival = new Date(departureTime.getTime() + durationInSeconds * 1000);
setArrivalTime(estimatedArrival);
}
}, [selectedRouteIndex, routes, departureTime]);
const handleRouteChange = (index) => {
setSelectedRouteIndex(index);
// Calculate new estimated arrival time
const selectedRoute = routes[index];
const durationInSeconds = selectedRoute.legs[0].duration.value;
const estimatedArrival = new Date(departureTime.getTime() + durationInSeconds * 1000);
setArrivalTime(estimatedArrival);
};
useEffect(() => {
if (directionsRenderer) {
directionsRenderer.setRouteIndex(selectedRouteIndex);
}
}, [selectedRouteIndex, directionsRenderer, routes]);
Enhancing UI with Map legend
Finally we add HTML to the UI with a Map legend to show origin and destination with departure and arrival time information with alternative routes.
const displayArrivalTime = () => {
return arrivalTime ? arrivalTime.toLocaleTimeString('en-US', {
hour: 'numeric',
minute: 'numeric',
hour12: true
}) : 'Calculating...';
};
const selectedRoute = routes[selectedRouteIndex];
const leg = selectedRoute ? selectedRoute.legs[0] : null;
if (!leg) return null;
if (!isOpen) return null;
return (
<div className="directions" style=>
<button onClick={toggleMinimize} style=>
{isMinimized ? 'Expand Legend' : 'Minimize'}
</button>
{!isMinimized && (
<>
<h2 style=>
{routes[selectedRouteIndex]?.summary}
</h2>
<p>
{leg.start_address.split(",")[0]} to {leg.end_address.split(",")[0]}
</p>
<p>Distance: {leg.distance?.text}</p>
<p>Estimated Arrival Time: {displayArrivalTime()}</p>
<div style=>
<label>Departure Time: </label>
<input
type="datetime-local"
value={toSingaporeTimeString(departureTime)}
onChange={handleDateChange}
/>
</div>
<h2 style=>Other Routes</h2>
<ul style=>
{routes.map((route, index) => (
<li key={route.summary}>
<button onClick={() => handleRouteChange(index)} style=>
{route.summary}
</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</>
)}
</div>
);
}
function MapLegend() {
return (
<div style=>
<h4>Traffic Conditions</h4>
<div><span style=></span> Smooth Traffic</div>
<div><span style=></span> Slow moving</div>
<div><span style=></span> Traffic jams</div>
</div>
);
}
export function renderToDom(container: HTMLElement) {
const root = createRoot(container);
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
}
Using LLM to show directions
This feature is very impressive and my teammate helped build this. It uses 6 different AI agents on user query to build an appropriate response which is shown on the map. These AI agents are:
- Emergency report generator: generates a emergency response report in case of an incident
- Report reader: Summarizes data and calculates the number of passengers affected
- Intention classifier: Identifies the intention of the query. Example if its an incident or asking for routes etc.
- Open chatter: Set up as a traffic guide/assistant
- Bus interchange query: Only used for recommendations involving bus interchanges
- Route query: Used for recommending routes from point A to B.
Execution Flow
When a query us asked by the user:
- Intention classifier function is triggered to know the intention
- If the intention is classified as general then Open chatter is used to provide traffic assistant
- If the intention is classified as emergency, then emergency report generator and report reader is triggered
- If the query contain - “show me a route from” then route query assistant is triggered.
The most important aspect of using these functions is prompt engineering.
Intention classifier
def intentionClassifier(text):
client = OpenAI(api_key=config["OPENAI_API_KEY"])
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content":
"""
You are an intention classifier.\n
Your task is to identify the type of intention of the query.\n
There are 3 possible types of intention: Describing Traffic Event, Requesting a Route, None of Above.\n
You must answer strictly according to the following rules:\n
If you think the intention of the query is Describing Traffic Event, you will return 1\n
If you think the intention of the query is Requesting a Route, you will return 2\n
If you think the intention of the query is None of Above, you will return 0\n
You must directly return the number without anything else.
"""
},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
)
try:
typeNumber=int(str(completion.choices[0].message.content))
if typeNumber not in [1,2]:
return(0)
return(typeNumber)
except:
return(0)
Open Chatter
def openChatter(text):
client = OpenAI(api_key=config["OPENAI_API_KEY"])
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content":
"""
You are a Singaporean Traffic Assistant.\n
Your user is a traffic planner, you will give suggestions from this perspective.
"""
},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
)
return(str(completion.choices[0].message.content))
Emergency report generator
def emergencyReportGenerator(text):
client = OpenAI(api_key=config["OPENAI_API_KEY"])
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content":
"""
You are an emergency response advice provider, and your clients are traffic authorities.\n
You provide emergency response suggestions.\n
If your answer contains MRT Station Name, provide its station code.\n
If your answer contains MRT Line Name, provide its line code.\n
If your answer contains bus stop name, provide its code.\n
You will predict at most 3 affected stations and/or stops. Provide number of passengers affected per hour for each station and/or stops you mentioned.
When predicting affected stations and/or stops, consider not only where the emergency occurred, but also the route-adjacent stations and/or stops.\n
Predict the types of emergency services the user needs to deploy and to which location in a separate paragraph. The emergency service types must strictly be: hospital, fire station, police station. However,if you think user don't need any of these services, omit this part.\n
Your answer should be as concise and professional as possible and should not contain any non-specific advice.\n
You don't need to explain your rationale.\n
No approximate values are allowed in your answer. If you cannot provide an exact number, provide a range bounded by the exact number.\n
"""
},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
)
returnText=completion.choices[0].message.content
client = OpenAI(api_key=config["OPENAI_API_KEY"])
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content":
"""
You are a data analyst serving for Singaporean transport system. You calculate and summarize data\n
The input is a emergency response report including several hourly numbers of passenger affected in several train stations and/or bus stops respectively.\n
You will devide those numbers by 102, then match each devided number with corresponding station or stop name.\n
You will list those devided numbers in following format: 1. name1 need devidedNumber1 extra bus trips per hour\n
You may not show calculations.
"""
},
{"role": "user", "content": returnText}
]
)
returnText=returnText+"\n\nBus Deployment Recommendation:\n"+completion.choices[0].message.content
return(returnText)
Report reader
def reportReader(reportText):
client = OpenAI(api_key=config["OPENAI_API_KEY"])
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content":
"""
You are a data preparation system. You serve Singaporean transport system\n
Your input will be a traffic emergency response report.\n
You will analyze which emergency services are suggested to be deployed to which destinations in this report\n
You should treat bus interchange as an emergency service if you notice the report mentions that there are passengers affected somewhere. However, when you are listing the results, you should put bus interchange later in the list.\n
If you think there is no emergency service included in this report, you need to strictly return:[[]]\n
Otherwise, your answer must strictly be in following format:[["emergencyServiceName1","destination1"],["emergencyServiceName2","destination2"],...]
"""
},
{"role": "user", "content": reportText}
]
)
try:
returnList=json.loads(completion.choices[0].message.content)
if len(returnList[0])==0:
returnList=None
except:
returnList=None
return(returnList)
Route query
def routeQuery(text):
modifiedText=busInterchangeQuery(text)
print("modified:"+modifiedText)
client = OpenAI(api_key=config["OPENAI_API_KEY"])
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content":
"""
You are a Navigation Assistant that is familiar with the Singapore map.\n
User will query you for a route. You will describe the route by specifying start place name and end place name.\n
User may use vague place names, including hospitals, fire stations, police stations. You need to search for specific place names to replace the vague place names.\n
Your response must strictly be in following format:[StartPlaceName#EndPlaceName]\n
"""
},
{"role": "user", "content": modifiedText}
]
)
#
returnText=str(completion.choices[0].message.content)[1:-1]
returns=returnText.split("#")
returns[0]=returns[0].replace(" ","+")
returns[1]=returns[1].replace(" ","+")
returns[0]="[\""+returns[0]+",+Singapore\","
returns[1]="\""+returns[1]+",+Singapore\"]"
returnText=returns[0]+returns[1]
print(returnText)
return returnText
Gradio App 📱
The last part is to put everything in a Gradio app with different pages and rendered map.
First we need to render the map from our react app to this app.
Connect react and gradio app
The function below fetches the localhost URL where the react app is running and show it in a iframe on this app’s page.
def generateHTMLText(routeQueryReturnText):
try:
host = os.getenv('HOST', 'localhost')
port = os.getenv('PORT', '8080')
base_url = f"http://{host}:{port}"
if routeQueryReturnText:
return f"<iframe src={base_url}/?body={routeQueryReturnText} width=100%% height=560px></iframe>"
else:
return f"<iframe src={base_url}/ width=100%% height=560px></iframe>"
except Exception as e:
return f"<iframe src={base_url}/ width=100%% height=560px></iframe>"
Free query UI
Next, we can define the free query UI element for the user.
def submitFreeQueryTextbox(history,text):
intentionTypeNumber=intentionClassifier(text)
print(intentionTypeNumber)
returnHtmlBox=None
reportText=None
dropDown=gr.Dropdown(choices=None,type='index',value=None,interactive=False,allow_custom_value=False)
freeQueryReportReaderReturnList=None
jsonText=None
if intentionTypeNumber==0:
reportText="""
***General Chat Mode***\n\
---Tips: If you wish to enter emergency report mode, you need to describe exactly what happened at where.---\n\n
"""
reportText=reportText+openChatter(text)
returnHtmlBox=gr.HTML(generateHTMLText(None))
elif intentionTypeNumber==1:
reportText="***Emergency Report Mode***\n\n"
reportText+=emergencyReportGenerator(text)
freeQueryReportReaderReturnList=reportReader(reportText)
print(freeQueryReportReaderReturnList)
if freeQueryReportReaderReturnList!=None:
choises=[item[0]+" TO "+item[1] for item in freeQueryReportReaderReturnList]
dropDown=gr.Dropdown(choices=choises,type='index',value=choises[0],interactive=True,allow_custom_value=False)
returnHtmlBox=submitQuickQueryTextbox("FROM",freeQueryReportReaderReturnList[0][0],"TO",freeQueryReportReaderReturnList[0][1])
else:
returnHtmlBox=gr.HTML(generateHTMLText(None))
elif intentionTypeNumber==2:
reportText="***Route Mode***\n\n"
reportText="Confirm!"
returnHtmlBox=gr.HTML(generateHTMLText(routeQuery(text)))
if freeQueryReportReaderReturnList!=None:
jsonText=json.dumps(freeQueryReportReaderReturnList)
returnList=[
history+[
[
text,
reportText
]
],
returnHtmlBox,
dropDown,
jsonText
]
#returnText=routeQuery(text)
return(returnList)
Helper functions
Helper functions to change, submit and load query URL.
def changeFreeQueryDropDown(index,jsonText):
print("debug index:")
print(index)
freeQueryReportReaderReturnList=json.loads(jsonText)
return(submitQuickQueryTextbox("FROM",freeQueryReportReaderReturnList[index][0],"TO",freeQueryReportReaderReturnList[index][1]))
def submitQuickQueryTextbox(quickQueryFromTo,quickQueryDorpDown,quickQueryToFrom,quickQueryTextbox):
text="Show me a route "+quickQueryFromTo+" a "+quickQueryDorpDown+" near "+quickQueryTextbox+" "+quickQueryToFrom+" "+quickQueryTextbox
print(text)
return(gr.HTML(generateHTMLText(routeQuery(text))))
def loadURLParams(request:gr.Request):
urlParamsDict=dict(request.query_params)
print(urlParamsDict)
selected=None
jsonString=None
returnFreeQueryTextbox=None
if 'tab' in urlParamsDict:
selected=urlParamsDict['tab']
del urlParamsDict['tab']
if 'query' in urlParamsDict:
returnFreeQueryTextbox=gr.Textbox(value=urlParamsDict['query'])
del urlParamsDict["query"]
if len(urlParamsDict)>0:
jsonString=json.dumps(urlParamsDict)
return([gr.Textbox(value=jsonString),gr.Tabs(selected=selected),returnFreeQueryTextbox])
The main page and launch
with gr.Blocks(title="BooleanPirates") as demo:
globalJsonBuffer=gr.Textbox(value=None,visible=False)
with gr.Tabs() as rootTabs:
with gr.Tab("Crisis Response",id="QuickQuery"):
with gr.Group():
with gr.Row():
with gr.Row():
quickQueryFromTo=gr.Dropdown(choices=["FROM","TO"],value="FROM",interactive=False,show_label=False,scale=1,min_width=60,filterable=False)
quickQueryDorpDown=gr.Dropdown(choices=[
"hospital",
"fire station",
"police station",
"bus interchange"
],value="hospital",interactive=True,show_label=False,scale=2,min_width=100,filterable=False)
with gr.Row():
quickQueryToFrom=gr.Dropdown(choices=["TO","FROM"],value="TO",interactive=True,show_label=False,scale=1,min_width=60,filterable=False)
quickQueryTextbox=gr.Textbox(show_label=False,scale=2,min_width=100,placeholder="Type here&Enter")
quickQueryHtmlBox=gr.HTML(generateHTMLText(None))
with gr.Tab("Open Query",id="FreeQuery") as freeQueryTab:
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(min_width=120):
freeQueryReportArea=gr.Chatbot(
value=[
[
None,
"""
Hello, I'm an emergency event report chatbot. You can either:\n
1) Describe a public traffic emergency, including what is happening and where, or\n
2) Query for a route from one location to another\n
\n
Currently, the traffic condition from SMU to NUS is shown as map.
"""
]
],
scale=1,
min_width=120,
show_label=False
)
freeQueryTextbox=gr.Textbox(show_label=False,placeholder="Enter to submit.Please ask for a route",scale=1,min_width=120)
with gr.Column(min_width=1080):
with gr.Group():
jsonTextBufferForReportReaderReturnList=gr.Textbox(value=None,visible=False)
freeQueryMapDropdown=gr.Dropdown(scale=3,show_label=False,interactive=False)
freeQueryHtmlBox=gr.HTML(generateHTMLText(None))
quickQueryToFrom.change(changeQuickQueryToFrom,quickQueryToFrom,quickQueryFromTo)
quickQueryTextbox.submit(submitQuickQueryTextbox,[quickQueryFromTo,quickQueryDorpDown,quickQueryToFrom,quickQueryTextbox],quickQueryHtmlBox)
freeQueryTextbox.submit(submitFreeQueryTextbox,inputs=[freeQueryReportArea,freeQueryTextbox],outputs=[freeQueryReportArea,freeQueryHtmlBox,freeQueryMapDropdown,jsonTextBufferForReportReaderReturnList])
freeQueryMapDropdown.input(changeFreeQueryDropDown,inputs=[freeQueryMapDropdown,jsonTextBufferForReportReaderReturnList],outputs=freeQueryHtmlBox)
demo.load(
loadURLParams,
outputs=[globalJsonBuffer,rootTabs,freeQueryTextbox]
)
demo.launch(server_name="0.0.0.0",server_port=8080)